What is osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine? How is lumbar osteochondrosis treated? And is it true that osteochondrosis is not treated at all?
Considering the statistics of morbidity, the number of cases does not decrease every year. Intervertebral osteochondrosis affects both a young organism and older people. How to treat osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, and the main symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis, will be described in detail by a neuropathologist or osteopath.
Osteochondrosis is a fairly common ailment. Malaise refers to a change in the shape of the vertebrae and a decrease in the elasticity of the intervertebral discs due to malnutrition of cells.
The lumbar spine suffers for a reason. Being in the lower part of the spinal column, the vertebrae take on the maximum load. When lifting weights, all the force acting on the body is fraught with depletion of the intervertebral space and this leads to compression of the nerve roots. From here, signs of lumbar osteochondrosis begin to appear.
Reasons
Each disease has predisposing factors that act negatively on the body. Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine also has its own causes. Doctors do not exclude the cause, transmission of the disease at the genetic level. It is believed that if parents have problems with malnutrition of the intervertebral discs, then there is a high probability that this problem will not bypass children. One of the most popular reasons is hard physical labor. When lifting weights, most of the load goes to the lumbosacral spine.
Obesity is an equally common cause of illness. The excess weight that accumulates in the body puts pressure on the spinal column and causes pain. It seems that bad posture will not lead to anything serious, but this is also one of the reasons for the wear of the intervertebral discs, which turns into osteochondrosis. Back injuries are important. Contusions, or the lifting of heavy objects by a poorly trained athlete, or an inaccurately matched load are also adversely affected.
The most common cause of poor nutrition in disc cells is a sedentary lifestyle.
In order to keep the body healthy, a person needs a moderate load. Limited or completely absent physical activity leads to a decrease in the speed of blood circulation. As a result, the muscles of the back, without receiving the necessary nutrients, weaken, and the load on the lumbar spine increases. Also, over the years, the spine becomes not as mobile as in youth, the elasticity of the intervertebral discs decreases, which leads to the disease.
Infectious diseases, or inflammation affecting bones or joints, lead to changes in the structure of the vertebrae. Congenital malformations of the skeleton, or deviations in the development of the musculoskeletal system. Flat feet, leads to the destruction of segments of the spine, due to the lack of shock absorption in the limbs. Most of the load falls not on the legs, but on the lower back, which leads to deformation of the segments. Stressful situations are a common cause of various diseases. Therefore, lumbar osteochondrosis and its symptoms are no exception. A strong nervous shock, can serve as an impetus for pinching the nerve endings, and cause an attack of pain. More often, stress is the cause of osteochondrosis in women, they are more prone to emotions than men.
Symptoms
The initial stage of the disease, doctors rarely diagnose. Therefore, it is difficult to identify the primary symptoms of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine. The manifestation of the disease occurs gradually.
Since the main manifestation is low back pain, there is a division of pain into 3 groups, which in turn characterize the symptoms and signs of low back pain.
- Lumbago- paroxysmal pain that occurs in response to a sudden movement, or weight lifting. When trying to take a different position, the pain becomes even stronger, up to lumbago.
- Lumbodynia- the pain increases and becomes regular. Muscle fibers and intervertebral cartilage are affected. Lumbodynia is a consequence of lumbago.
- Lumboishalgia- painful sensations, cold or heat in the lumbar region and lower limbs. They arise in response to pinching of the roots of the spinal cord.
The second most important symptom in diagnosing a disease is the limitation of physical activity, due to painful sensations. When trying to do a work or exercise habitual for oneself, a person experiences increased pain, which can affect the entire leg. Even in a seated position, the patient experiences tingling sensations from the lower back to the foot.
Equally important is a local decrease in temperature and discoloration of the skin, it becomes dry and pale. Numbness, weakness in the muscles of the lower extremities, indicates the progression of the disease. The most severe phenomenon, manifested in the last degree of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, is a dysfunction of the pelvic organs. To constant debilitating pains, incontinence of feces and urine, or vice versa, a delay in excretion join.
When diagnosing diseases, there are four stages of osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine. For each stage, symptoms of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine are characteristic, to which pains in the sacrum are added.
In the process of disease progression, osteochondrosis can descend to the final spine, the tailbone. The disease is called osteochondrosis of the sacral spine. There are acute, paroxysmal pains in the coccyx area. Women suffer the most in this case. Their anatomical structure of the body, and age-related changes in it, contribute to the development of intervertebral osteochondrosis. Osteochondrosis in women is often complicated by other internal diseases.
Symptoms of lumbosacral osteochondrosis have some difference from lumbar osteochondrosis.
Symptoms manifest themselves in dysfunction of the pelvic organs, making it difficult to select the correct treatment and diagnose the cause of the disease.
Signs such as frequent urination, urinary and fecal incontinence appear. If the diagnosis is not correct, complications arise.
Stages of the disease
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis also differs from the stage of the disease.
- The first, and it is the initial stage of the disease, is characterized by the manifestation of pain in the lower back - lumbago, muscle spasm, local swelling of the skin.
- Secondstage, begins with lumbodynia. The pains become regular and more intense than in the initial stage. In the joints of the spine, an uncharacteristic mobility may appear, which increases pain. The pain is felt along the sciatic nerve. Less commonly, the functions of internal organs may be impaired.
- The thirdstage is characterized by the appearance of intervertebral hernias. The spine is deformed, Curvature can be left or right, this is scoliosis, forward - lordosis, backward - kyphosis. Due to this, a person is tormented by constant sharp pains.
- Fourthstage, the most difficult. Due to constant severe pain, the patient's movement is difficult. Without starting treatment on time, a person may be permanently disabled.
Complications
The most common complication is dysfunction of the genitourinary system. Together with incontinence, urine and feces, inflammation occurs in the urine-genitals, and in the rectum. With a more pronounced lesion of the vertebrae, irritation occurs in the direction of the sciatic nerve, and its inflammation. Intervertebral disc protrusion is a very dangerous complication. Protrusion is a borderline condition of the intervertebral disc, which can lead to the next complication if treatment is not started on time. It occurs due to a passing degenerative change in the spine.
The consequence of protrusion is a herniated disc. Which is manifested by a change in its shape, and a rupture of the membrane of the intervertebral disc.
Constant compression of the nerve roots of the spinal cord and inflammation leads to such a complication as radiculitis.
Complete obstruction of the spinal canal may occur. Due to instability in the lumbosacral region, men develop congestion in the small pelvis, which leads to impotence. In women, this leads to inflammatory diseases of the uterus, ovaries and appendages. From the side of the kidneys, this is renal colic, which cannot be eliminated until osteochondrosis of the lower back is treated. Paralysis of the lower extremities, which can confine a person to a wheelchair. Timely diagnosis and timely treatment of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine helps prevent these complications and avoid disability.
Treatment
Let us examine lumbar osteochondrosis, symptoms and treatment. In modern times, medicine is able to achieve the recovery of a person suffering from osteochondrosis. Treatment of osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine takes a long time. A sick person, who has intervertebral osteochondrosis for the first time, will still wonder whether it is possible to cure osteochondrosis, and how to get rid of it forever?
What to do? Is osteochondrosis of the lower spine treated? First you need to completely revise your lifestyle. Draw certain conclusions. You need to move towards the cherished goal of healing every day without interruption. With osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, complex treatment of the disease is of great importance. Treatment of lumbosacral osteochondrosis includes several methods.
Conservative
Conservative treatment, based on massage techniques, which, if done correctly, can relieve muscle spasm and improve the nutrition of muscle fibers. By improving trophism, the corset of the back muscles is strengthened. Posture takes the correct position, which determines the appearance of various problems with the spine. Physical therapy for lumbar osteochondrosis is very useful, but you need to exercise during the period of remission, between exacerbations. Engaged in the acute period of the disease, you can only aggravate the situation and harm your health.
Manual therapy also refers to conservative treatment. It should be performed by a professional specially trained in this technique. Thanks to this therapy, the spine can be returned to the desired position. This is sometimes the most effective method. It is necessary to carry out such a procedure in the subacute period.
Eating diets, obese people, leading a healthy lifestyle and adhering to a healthy diet will not hurt anyone. And people with such ailment will only benefit. Since being overweight, this is one of the reasons for the appearance of osteochondrosis. Physical therapy is an equally effective treatment. Magnetotherapy, UHF are capable of long-term treatment, improve blood circulation in the affected area with lumbar osteochondrosis. They also have a vasodilating and analgesic effect.
Medication type of treatment. How to cure osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine with medication? What treatment should be, all these questions are of great interest to a sick person. Treatment is divided into two types. In the first case, during the acute period of intervertebral osteochondrosis, drugs are aimed at eliminating pain and inflammation. Means are used that release the pinched roots of the spinal nerves. These include muscle relaxants, glucocorticosteroids, blockades, NSAIDs. For the second period, between exacerbations, drugs are used to improve blood circulation, restore muscle and nerve fibers, damaged body tissues. For this purpose, vitamins and preparations of plant and animal origin are used.
To improve blood circulation, vascular preparations, as well as warming and anesthetic ointments, are used.
Operational
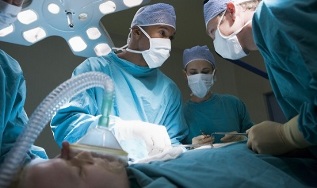
Neurosurgeons perform microsurgical and endoscopic operations on the spinal column.
These methods are more common and are removed when other treatments fail.
When the effect of drug therapy has not been achieved, and complications such as hernia appear, surgery to remove the affected disc is indicated.
Disease Prevention
Prevention of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine consists in eliminating the risk factors leading to this disease. In order not to think about how to cure lumbar osteochondrosis, you need to prevent its occurrence. Eliminating the causes is the main preventive measure.
Normalized physical activity, strengthening the back muscles, preventing the maximum load on the lumbar spine, preventing the development of diseases leading to osteochondrosis, all these are preventive measures to prevent the symptoms of lumbosacral osteochondrosis. By adhering to these simple principles, you will maintain your health and prolong life. After all, without observing treatment and prevention, you may never return to a full life.



































