Back pain in the lumbar region is familiar to everyone. According to statistics, it is she who becomes the cause of 25% of all requests for medical care. Its appearance can provoke a lot of different factors from banal fatigue to quite serious diseases. Therefore, you should not ignore the problem, especially if the discomfort appears regularly and even more so over time. In such situations, you should contact a therapist as soon as possible or go directly to a neurologist and undergo a comprehensive examination. This will allow diagnosing the disease in the early stages of development and taking timely measures to stop its progression. But if on the eve of the onset of pain there was an injury or an unsuccessful fall, you need to sign up for a consultation immediately to a traumatologist or a spinal surgeon.
This will allow diagnosing the disease in the early stages of development and taking timely measures to stop its progression. But if on the eve of the onset of pain there was an injury or an unsuccessful fall, you need to sign up for a consultation immediately to a traumatologist or a spinal surgeon.
Features of low back pain and accompanying symptoms
Back pain can be of different nature and severity. They can be strong, shooting, aching, pulling, etc. They can intensify during physical exertion, sitting or standing for a long time, and pass at rest or not. All these are important diagnostic factors that allow the doctor to make the correct diagnosis and find the true cause of the patient's condition.
Of fundamental importance in making a diagnosis is whether the pain radiates to the hip, buttock, knee, foot, and if so, where and how. Also, a weighty point is the presence of restrictions on the mobility of the spine, whether the patient can freely make bends, body turns, or the range of motion is reduced.
Pain in the spine is called lumbodynia. If it spreads to the legs, it is called lumboischialgia.
Acute pains are those that persist for less than 3 months; otherwise, they speak of chronic pain. In the latter case, the disease often proceeds with periods of exacerbation and remission.
Low back pain rarely occurs in isolation. In most cases, a complex of other disorders is additionally present, which the patients themselves rarely associate with each other. Often, back pain is combined with:
- feeling of crawling in the back and / or legs, numbness;
- muscle weakness;
- pain in the hip, knee joints;
- disruption of the pelvic organs (menstrual irregularities, problems with potency, loss of control over urination, defecation);
- leg paralysis.
Similar signs indicate pathology of the spine. But since not only they can provoke the appearance of back pain, there is another group of symptoms that can accompany lower back pain and indicate the pathology of internal organs or cancer. Therefore, you need to be especially careful about your own state when it appears:
But since not only they can provoke the appearance of back pain, there is another group of symptoms that can accompany lower back pain and indicate the pathology of internal organs or cancer. Therefore, you need to be especially careful about your own state when it appears:
- rapid and unnecessary weight loss;
- cuts and pains in the groin, perineum;
- increased urination, soreness;
- increase in body temperature, chills;
- changes in skin color in the area of the epicenter of pain;
- menstrual irregularities, unusual discharge.
If lower back pain is associated with one or more of the above symptoms, you should see a doctor immediately. When symptoms appear from the first group, consultation of a neurologist is required, from the second, the help of a urologist, gynecologist, endocrinologist or other narrow specialists is needed. The therapist will help you to understand exactly which doctor to contact.
Causes of occurrence
All causes of back pain in the lumbar region can be divided into 2 groups: diseases of the spine and pathologies of internal organs, in particular, gynecological diseases, pathologies of the kidneys, gastrointestinal tract organs, endocrine disorders. But still, most often they are a consequence of the development of changes in the spine and the muscles surrounding it. The most common causes of back pain are:
- osteochondrosis;
- spondylosis;
- inflammatory diseases of the spine;
- myofascial syndrome;
- ankylosing spondylitis;
- scoliosis;
- injuries.
However, lower back pain can also be the result of overwork or certain physiological changes. In such situations, they do not require special treatment, but only a reduction in physical activity and a more sparing day regimen.
Osteochondrosis and intervertebral hernias
Osteochondrosis is the most common disease of the spine. Its development is often associated with inevitable age-related changes, since almost every elderly person has its symptoms to a greater or lesser extent.
Osteochondrosis is humanity's price to pay for the ability to walk straight. It is characterized by the gradual destruction of the intervertebral discs, their thinning, a decrease in elasticity and firmness. As a result, they cease to cope with the stress and may bulge. Thus, intervertebral hernias are formed.
Most often, osteochondrosis affects the intervertebral discs of the lumbar spine. When they protrude into the spinal canal or foraminal foramen, the nerves are almost inevitably impaired, which leads to the appearance of acute pain in the lower back and their irradiation to the legs and buttocks.
Spondylosis
Spondylosis is a complication of advanced osteochondrosis, in which the intervertebral discs are almost completely destroyed, and due to the ongoing degenerative processes and an increase in the load on the spine along the edges of the vertebrae, bony protrusions called osteophytes are formed. Therefore, there is a high risk of crushing and injury to nearby nerves. This causes severe pain that can radiate to the legs.
Therefore, there is a high risk of crushing and injury to nearby nerves. This causes severe pain that can radiate to the legs.
Inflammatory diseases of the spine
Most often, inflammatory diseases of the spine occur in young people, and mainly in men. They cause severe pains that bother even at night, which is their specific difference. As it progresses, in the absence of timely treatment, the pain becomes more intense and bothers the person more often.
It is not uncommon for patients to seek medical help several years after the first symptoms appear. As a result of such a long course of the inflammatory process in the spine, irreversible changes can occur, which can ultimately lead to immobility and disability.
Sometimes, in addition to lower back pain, there is discomfort in the joints of the legs and arms. In such cases, the cause of discomfort may be arthritis, osteomyelitis.
Myofascial syndrome
Myofascial syndrome is a common pathology in which pain occurs after a prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position or after physical exertion. Slightly more often, myofascial syndrome occurs in women. With it, lower back pain occurs after careless movement or physical exertion. Its distinguishing feature is the presence of so-called trigger points on spasmodic muscles in the lumbar region and buttocks, pressing on which leads to a sudden attack of pain. Myofascial syndrome significantly reduces the quality of human life, but does not pose a serious threat.
Bechterew's disease
Ankylosing spondylitis or ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic joint disease in which the sacroiliac joint, the joints of the spine and the surrounding soft tissues are primarily affected. With this disease, people are worried about back pain and sacrum pain and stiffness of movements, but the symptoms usually disappear without a trace in the afternoon and at night.
In addition, physical activity has a beneficial effect on the patient's well-being and contributes to the elimination of pain syndrome. Quite a specific symptom of ankylosing spondylitis is stoop, arcuate curvature of the spine and progressive limitation of mobility.
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a lateral curvature of the spine. It can be of varying severity, which directly affects the intensity of back pain and other symptoms. Since the deformity of the spine leads to a displacement of all anatomical structures, the nerves are often pinched, which causes severe pain. In addition, other neurological signs may be present, including a feeling of numbness and paresis.
Compression fractures
In older people with osteoporosis and trauma, lower back pain may be the result of an undetected spinal compression fracture. As a result, the vertebrae are flattened and occupy an abnormal position, which leads to an incorrect distribution of the load on the spine, degenerative processes in the intervertebral discs and the appearance of pain.
Physiological causes of low back pain
Performing hard physical work, intense sports training creates an increased load on the muscles, as a result of which lactic acid accumulates in them, which provokes pain. Back pain is not uncommon with prolonged wearing of uncomfortable shoes, especially with heels.
Also, lower back pain is often observed during pregnancy. In such situations, they are caused by a shift in the center of gravity and increased stress on the spine.
Diagnostics
To determine the causes of back pain in the lumbar region, it is recommended to consult a neurologist. Initially, you can get a consultation from a therapist, but, most likely, the doctor will still refer the patient to a neurologist.
At the appointment, the specialist will conduct a thorough survey of the patient, find out what worries him, what kind of lifestyle he leads, etc. Further, an examination is required, during which the doctor assesses the severity of reflexes, conducts neurological tests and evaluates the patient's mobility. Based on the results obtained, the doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis and understand what kind of violations led to the onset of back and lower back pain.
To confirm the existing assumptions, to determine the exact causes of pain, a comprehensive examination of the patient is carried out, which may include:
- general and biochemical blood tests - with their help, changes in the blood are detected, indicating inflammatory processes in the body, the presence of an infection or tumor;
- general urinalysis - used to differentiate kidney diseases as the cause of pain in the lumbar region;
- X-ray - shows the presence of a change in the bone structures of the spine, signs of fractures, gives information about bone density and allows you to diagnose major diseases of the spine, as well as osteoporosis (detection of pathologies of the spine is a reason for a more thorough examination using CT or MRI);
- CT is a modern method of radiation diagnostics, which allows you to very clearly visualize all bone structures and detect the slightest deviations from the norm;
- MRI - provides comprehensive information about the state of soft tissues and cartilage, including intervertebral discs, using MRI you can diagnose intervertebral hernias of any size, changes in blood vessels, tumors.
Low back pain treatment
Treatment of back pain is selected strictly individually. At the same time, it is always complex and includes symptomatic therapy, lifestyle changes and treatment aimed at eliminating the found causes of lower back pain. Therefore, if the first 2 components of therapy are usually universal and are prescribed to all patients, then etiotropic therapy is developed strictly individually, taking into account the existing disease.
In most cases, patients are initially offered conservative treatment, the main component of which is drug treatment. In more complex cases, it is additionally recommended to conduct a course of physiotherapeutic procedures, manual therapy and exercise therapy.
But in any case, all patients with low back pain should:
- give up lifting heavy objects and exhausting sports;
- to reduce weight in the presence of obesity;
- take regular breaks to warm up if a person is forced to sit for a long time;
- to increase the level of physical activity, but avoid overwork and doing hard work (daily walks, morning exercises, performing a special exercise therapy complex, swimming);
- to use a support bandage, which will relieve the load on the lower back and thereby provide favorable conditions for the early recovery of the spine.
Depending on the source of pain, patients may be advised to stay in bed for a couple of days or, on the contrary, increase their level of physical activity, but within reasonable limits. For example, pain caused by nerve compression requires you to rest your back for a few days. In other diseases, on the contrary, moderate physical activity is one of the mandatory components of therapy. It helps to increase the effectiveness of drug treatment, reduce the risk of complications and prevent disability.
Unfortunately, conservative therapy cannot always be used to treat low back pain. In some cases, it turns out to be ineffective and does not give any results even after several months of unswerving adherence to medical recommendations. In other situations, the examination results show the presence of pathology that can no longer be eliminated by any non-surgical methods. In such situations, patients are advised to consult a neurosurgeon and carry out appropriate surgical intervention to restore the normal anatomy of the spine.
Drug therapy
To improve the patient's condition and quickly relieve pain, the following are prescribed:
- NSAIDs in the form of tablets, injections and topical preparations - have analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties;
- corticosteroids - given in short courses to control severe inflammation;
- muscle relaxants - necessary to relieve muscle spasm, which is often a reflex reaction of the body to pain and aggravates it;
- B vitamins - improve nerve conduction by normalizing the nutrition of nerve fibers and increasing the speed of transmission of nerve impulses.
For severe pain that cannot be tolerated, blockages can be performed. The procedure involves injecting an anesthetic solution directly into the area of pain or nerve fiber passage. Thus, it is possible for a while to completely stop the pain syndrome and improve the patient's well-being.
But the blockade has only a temporary effect, and its implementation is possible only in a medical institution, since most often it is required to inject the drug into points located in the immediate vicinity of the spine, where a mass of nerves passes. Therefore, an illiterate execution of the procedure can result in severe and sometimes fatal consequences.
In addition to the medications listed above, a set of others is prescribed, which help to eliminate the underlying disease that caused the pain syndrome. Therefore, patients can also be prescribed antibiotics, chondroprotectors, immunomodulators and drugs of other groups.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy treatments are often prescribed for patients with spinal disorders. Thanks to the correctly selected method of physical influence and the frequency of procedures, it is possible to achieve a pronounced anti-inflammatory, analgesic effect, as well as improve microcirculation, accelerate the elimination of local edema, muscle spasms, etc. Physiotherapy significantly increases the effectiveness of other treatment methods, but is mainly used only after the elimination of acuteprocess.
Most often, patients are prescribed:
- electrophoresis;
- UHF;
- ultrasound therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- reflexology;
- diadynamic currents, etc.
As a rule, the course of procedures includes 8-10 sessions, which are carried out with a certain frequency.
Manual therapy
With osteochondrosis, scoliosis and a number of other diseases, manual therapy sessions can have a truly amazing effect on the condition of the spine. But only a qualified chiropractor can competently conduct a manual therapy session and benefit the patient, not harm.
The use of special techniques of manual exposure allows to achieve not only an improvement in microcirculation, relaxation of overly toned and too relaxed muscles, but also an increase in the distance between the vertebrae, as well as normalization of their position. A qualified chiropractor is able to find the place where the nerve is pinched and relieve the pressure of the anatomical structures on it.
Literally, after the first session, the majority of patients notice an improvement in their well-being and a significant decrease in the severity of the pain syndrome until it is completely eliminated. But to consolidate the results obtained, it is recommended to undergo a full course of manual therapy, and in the future to take supporting courses.
exercise therapy
Physical therapy helps the body to cope with the stress placed on it. For each disease, a special set of exercises has been developed, the regular implementation of which allows solving the most important tasks in the current situation. So, with the help of a properly selected complex of physiotherapy exercises, it is possible to bring back muscles to normal tone and strengthen them. Thanks to this, the spine will have less stress, which will be an effective prevention of the progression of the disease and create favorable conditions for its recovery.
Exercise therapy also helps to improve blood circulation in the affected area, which accelerates the course of inflammatory processes and sooner leads to a complete recovery. Correct exercise for many conditions can help reduce back pain and reduce the frequency of its occurrence.
The training program is developed individually for each patient. This takes into account not only the type of pathology detected and the degree of its severity, but also the presence of concomitant diseases, the level of physical fitness of the patient, his age and other factors. Only a specialist is able to choose the most effective and safe set of exercises correctly.
It is under his supervision that the first classes are held. In the course of them, the patient learns to correctly perform each proposed exercise so that it is beneficial. Gradually, the load is increased, bringing it to the optimal level. But it is not recommended to increase the number of repetitions of exercises yourself or to complicate them. Any changes to the physical therapy program are introduced only by a specialist.
The patient only needs to strictly follow his recommendations and practice daily in a comfortable environment. All exercises are performed at a slow pace. Any sudden movements are not allowed. But if pain arises during the lesson, the exercise should be stopped immediately and consult your doctor as soon as possible.
Surgery for back pain
Most often, the help of a spinal surgeon is necessary for intervertebral hernias, the formation of which has led to the infringement of the spinal root and the development of radicular pain. If the bulge has already formed, it is impossible to force it to be pulled back in modern non-invasive ways. The only way to eliminate it and at the same time to get rid of lower back pain is to remove the intervertebral hernia by surgery.
There are several types of surgeries used for intervertebral hernias. The specific tactics of surgical intervention is determined based on the type, location and size of the hernia:
- Nucleoplasty and hydroplasty are methods of percutaneous surgery that allow removing a part of the nucleus pulposus through a puncture of tissues with a diameter of several centimeters and reducing the size of the hernia.
- Microdiscectomy is a radical way to solve the problem of an intervertebral hernia, implying the removal of it or the entire disc through an incision up to 3 cm long. But, unlike other methods, it allows you to eliminate a hernia of any size, regardless of its location in the spinal canal, and releasea pinched nerve even in the most difficult part of the spine.
- Endoscopic surgery - involves the removal of a disc herniation through puncture punctures up to 1 cm in diameter using special equipment with a video camera. It can be used to resect hernias of any size, but the technique cannot be used to remove neoplasms in anatomically difficult places.
Also, the help of a spinal surgeon is needed for scoliosis. In this case, all forces are directed to restore the normal axis of the spine. Previously, this required making a large incision extending across virtually the entire back. But today it is possible to correct the deformity of the spine in a minimally invasive way through miniature incisions.
Various types of metal structures are used to restore the normal axis of the spine, but their essence is approximately the same. The structure is fixed on the vertebrae with special screws and by correcting its tension at different points, it is possible to return the displaced vertebrae to their place and fix them in the correct position. Modern types of metal structures allow, over time, to improve the initial result of the operation without re-intervention in the body. This is achieved by correcting the position of the installed structure using special screws.
Surgical intervention can not be avoided in case of spinal fractures. In such situations, getting rid of back and lower back pain is possible only by restoring the normal shape, size and position of the vertebrae. Recently, kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty have been performed for this purpose. The essence of both operations boils down to the fact that through a thin puncture needle, a special bone cement is injected into the vertebra destroyed as a result of an injury. 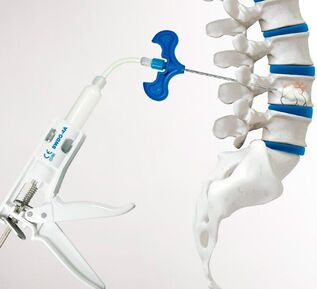 It fills all the free space and hardens after 10 minutes. But in severe compression fractures, kyphoplasty is preferred, since it can also help restore the normal shape of the vertebra, which will ensure the correct distribution of the load on the spine in the future and reduce the risk of complications. This operation involves the preliminary introduction of a special balloon into the destroyed vertebra, which is gradually inflated, returning the vertebra to its original appearance. After that, the balloon is lowered and removed, and the formed cavity is filled with bone cement.
It fills all the free space and hardens after 10 minutes. But in severe compression fractures, kyphoplasty is preferred, since it can also help restore the normal shape of the vertebra, which will ensure the correct distribution of the load on the spine in the future and reduce the risk of complications. This operation involves the preliminary introduction of a special balloon into the destroyed vertebra, which is gradually inflated, returning the vertebra to its original appearance. After that, the balloon is lowered and removed, and the formed cavity is filled with bone cement.
Thus, back pain can be the result of physiological changes, common muscle fatigue, or a symptom of serious pathologies of the spine or internal organs. Therefore, if they occur regularly and especially against the background of the action of the same factors, you should not hesitate and ignore the problem. Contact qualified specialists so that the treatment is as fast and easy as possible. And if the disease could not be recognized at the early stages of development, the modern level of neurosurgery will make it possible to eliminate it surgically with a minimal risk of complications.



































