Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease characterized by slow and progressive destruction of articular cartilage. Arthritis includes a group of joint diseases destructive and inflammatory nature, which have different causes and similar development mechanisms.
Osteoarthritis is one of the most common diseases in the world, occupying the leading position in women and men over the age of 30, and with age the risk of developing the disease only increases.
The causes of pathology
Osteoarthritis develops as a result of a violation of metabolic processes in the joints, against which intra-articular cartilage begins to lose water and becomes elastic. Contributing factors of such changes in cartilage can be internal and external reasons:
- hormonal changes;
- age features;
- genetic predisposition;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- excessive load on the joints;
- the trauma and injuries – sprains, fractures, bruises, torn ligaments;
- changes in metabolism within the joint, associated with obesity, diabetes;
- hypothermia;
- inadequate and unbalanced nutrition, causing the body loses calcium, omega-3 and 6 fats and proteins;
- the inflammatory process in the joint;
- violation of blood supply of the femoral head – Perthes disease;
- problems with blood clotting, inherited disease;
- autoimmune diseases – lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis.
To trigger the development of osteoarthritis can also specific diseases, which have nothing to do with joints, namely:
- gonorrhea;
- syphilis;
- hyperthyroidism;
- thyroiditis.
At risk are people who engage in heavy physical labor, forced hypothermia, and experience increased stress on the musculoskeletal system – miners, Smiths, athletes, movers and pregnant women.
The symptoms of osteoarthritis
The first symptom of osteoarthritis is pain at the slightest stress on the joint, which passes quickly, as soon as the joint is left alone. Osteoarthritis is characterized by 4 major clinical signs:
- Pain – pain when osteoarthritis has some features unlike pain accidental injury of the joint or inflammation in it. First of all, you should pay attention to the occurrence of discomfort and pain at any movement and load on the affected joint. There is a person to stop the movement and remove the strain, as the pain goes away just like that, which is not possible in trauma or inflammation of the joint. In the night, collapsing the joint virtually does not cause the patient discomfort, and pain is only possible when you change the position of the body, but they quickly pass. In severe progression of destructive processes in joints at night may experience sharp shooting pains, which will eventually become stronger and make adjustments to lifestyle. Acute pain occurs with any change in weather, the changing phases of the moon, the slightest exertion.
- Crunch – the sound is the result of a decrease in the softness of the rotation of the bones around the joint, which leads to rubbing of bones against each other and accompanied by the characteristic crunch. Progression of degenerative processes in the joint, the crunch becomes more pronounced and is accompanied by pain.
- Limitation of joint mobility – at the initial stage of development of the pathological process the expressed restriction of mobility there, but as the progression of the destruction of the joint inside the patient harder to do simple actions. Eventually the affected joint is completely immobilized.
- Deformation of the joint – on the bone surfaces are beginning to grow osteophytes and synovial fluid accumulates. Deformation of the joint is observed in the running extent of the pathological process.
Degenerative processes in the joint do not develop quickly, the disease is characterized by stages of exacerbation and remission, from what patients are reluctant to seek medical help, thereby contributing to the progression of destructive processes within the joint.
Stage
The stage of progression of the pathological process in the joint is determined by using x-rays. Allocate only 4 stages of the disease:
- The first is characterized by a slight narrowing of the joint space, with no pathological growths on the bone there;
- Second – there is a slight narrowing of the joint space on the surface of the bone osteophytes are formed;
- Third – the joint space is narrowed, on the surface of the bone multiple osteophytes, has a deformation of the joint;
- Fourth – articular slits are almost there, there are multiple osteophytes, severe deformation of the joint.
Degree
Osteoarthritis is expressed in the form of degenerative and destructive processes in the joint which affects the cartilage, develop changes in the capsule and synovial membrane of the joint and the ligaments around it and bone structures. Depending on the severity and intensity of these destructions it is accepted to allocate 3 degrees of osteoarthritis.
First degree
Expressed deformation or change in the joint no, but disturbed synovial fluid – this leads to the insufficient provision of joint tissues with nutrients, water and minerals, causing the cartilage quickly becomes not flexible and not adapted to the loads. Over time, this causes inflammation and is accompanied by pain with movement and stress on the joint.
At the first degree of osteoarthritis one of their patients do not seek medical care, writing off the discomfort and pain in an uncomfortable position during sleep, fatigue, unhealthy lifestyle. Sometimes the patient may notice a characteristic crunch in the affected joint, but this is not accompanied by severe pain, but only discomfort, again, no one pays much attention.
If the osteoarthritis is diagnosed by accident in the first stage, disease is easily treatable.
Second degree
At this stage, the disease is accompanied by destructive processes in cartilage tissue in joints. On the surface of the bone strenuously grow osteophytes, and the more intense the load on the affected area, the more pronounced will progress destruction.
This patient complains of constant aching pain and shooting character, which are held periodically by themselves and can a long time to make itself felt. Then the disease progresses again. Against the background of pathological process the muscles that surround the inflamed joint, gradually lose their functions, causing the patient tires easily and cannot withstand the physical stress that easily endured before. At the second degree of osteoarthritis, the patient gradually progressing deformity of the cartilage and joint.
Third degree
Is the most severe. Intra-articular cartilage of the affected joint thins and hard breaks, which leads to a clearly visible deformation and dysfunction of the affected limb. Located next to joint ligament and missty experiencing a shortage of nutrients and oxygen and gradually atrophy that is accompanied by severe loss of mobility. In this case, patient all the while suffering from acute pain, which increases with any attempt to change the position of the body when the weather changes and moon phases and gradually leads to complete loss of function.
Types of arthritis
Depending on what the cause triggered by a pathological process inside the joint there are primary osteoarthritis, secondary and idiopathic.
Primary develops as an independent disease, secondary as a consequence of trauma or infection, and the cause of the idiopathic form is not known. In addition to classification of the disease depending on the causes of the pathological process distinguish osteoarthritis at the site of localization of destructive changes:
- Gonarthrosis is the most common type of pathology characterized by a lesion of the knee. Osteoarthritis most often detected in people with obesity, chronic diseases of metabolism in the body, weak immune system. Knee osteoarthritis progresses for a long time and gradually leads to complete loss of motor function.
- Osteoarthritis ankle – the main reasons of development of degenerative processes in the ankle are injuries, sprains, strains, fractures. In some cases the pathological process may trigger autoimmune disease – rheumatoid arthritis. Ankle arthrosis is exposed to dancers, women wearing high heels, athletes.
- Shoulder joint arthrosis is the main cause of degenerative processes in this phase are congenital abnormalities of the shoulder joint or excessive load on the zone, for example, when carrying heavy Luggage on shoulders.
- Coxarthrosis, or arthrosis of the hip joint – the main cause of appearance are the age-related changes in the tissues of the joint. At risk are people over 45 years old.
- Encountres or arthrosis of the cervical – causes are injuries to the neck, progressive low back pain, obesity, sedentary lifestyle. At risk people working at the computer in the office. In addition to expressed pain in the neck in patients with marked dizziness, depression of consciousness, impaired memory and fatigue. These symptoms are caused by compression of the vertebral artery, through which the brain receives nutrients and oxygen.
- Spondiloarthrosis – destructive destruction of the affected tissue of the spine, namely the lumbar of his Department. At-risk women in the period of menopause, as the spondylosis progresses on the background of deficiency of female sex hormones.
- Osteoarthritis of the fingers – develops for the same reason that the spondylosis.
- The polyarthrosis – characterized by involvement of multiple joints with progressive degenerative processes in them, while in the pathological process involved ligaments, muscles and the tissues around the joint.
Possible complications
In the absence of timely diagnosis and treatment osteoarthritis will progress to involve other joints, promote the development of gruzevich protrusions and development total polyarthrosis.
Complications of osteoarthritis are the following States:
- the destruction of the integrity of the joint;
- shape deformation;
- the limitation;
- disability of the patient.
All of these complications lead to a significant decline in the quality of life of the patient, attach related diseases and disorders, fully immobilize the patient.
Diagnostic methods
For the diagnosis of the disease, the patient should seek the assistance of the traumatologist-orthopedist. In order to differentiate osteoarthritis from other pathologies of the joints and musculoskeletal system is prescribed x-ray in 2 projections. This study helps to pinpoint the modified portions of the tissues adjacent to the affected joint, the presence of damage in the bones and ligaments, osteopenia sprawl.
If necessary, the doctor may additionally prescribe MRI, CT scan and arthroscopy. In some cases, produce a puncture of the joint for specimen collection synovial fluid.
Treatment of osteoarthritis
The treatment of arthritis is best done in the early stages, then the disease better responds to conservative therapies. It is important to establish the cause of progressive destructive changes in the joint and in time to arrest these factors.
Treatment of osteoarthritis is complex and involves the elimination of the inflammatory process, relieve pain, halt progression of the pathological process and the restoration of the lost functions of the joint. Conservative therapy includes the selection of drugs and physiotherapeutic methods of treatment.
Medication
Treatment of osteoarthritis varies in different places of localization of the pathological process:
- Osteoarthritis of the fingers and hands – the patient to reduce pain prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of ointments, cream, gel. To prevent the progression of pathological process is shown receiving chondroprotectors. After relief of the acute inflammatory process prescribed massage and physiotherapy treatments.
- In case of arthrosis of the shoulder joint into the joint injection, the patient painkillers and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Oral can schedule an appointment antispasmodic drugs that will relax the muscles and reduce some of the intensity of the pain. After the relief of acute inflammation and pain shown therapeutic physical training and massage.
- Osteoarthritis of the knee – administered non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs topically in the form of compresses, ointments, gels. On the affected joint shown physiotherapeutic therapies.
- Osteoarthritis of the hip joint – to the affected area apply compresses soaked in the ointment or gel from the NSAID group, and inside of the joint is injected with painkillers injection.
- Osteoarthritis of the knee on the affected area is applied creams and gels with the analgesic effect, and after the relief of acute pain and inflammation shown physical treatment methods.
- Ankle osteoarthritis – the patient is recommended strict bed rest with maximum rest to the affected joint. With the subsiding of acute inflammatory process are assigned physiotherapy, baths and massages.
Physiotherapy treatment
To effective physiotherapeutic methods frequently used in various degrees of severity of osteoarthritis include:
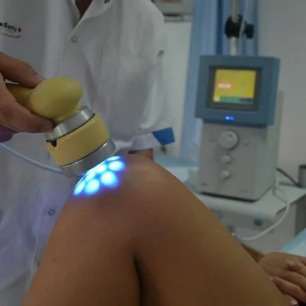
- Shock wave treatment effectively relieves the patient from the growths osteophytes, thereby eliminating the pain and limitation of joint mobility;
- Stimulation of the muscles around the affected joint by electric currents, this procedure is very effective for patients with severe reduced mobility and helps to improve blood circulation in the joint, accelerate regenerative processes, improve muscle tone;
- Ozone therapy, in the cavity of the affected joint gas mixture is introduced, thereby decreasing the patient pain, normal joint flexibility, fade the signs of inflammation. For maximum effect, ozone therapy courses are conducted;
- Phonophoresis – the impact on the affected area by ultrasonic waves with the use of drugs. This method of medication is much more effective, since ultrasonic waves deliver the drug directly to the lesion.
In addition to physiotherapy treatment includes physical therapy, massages, manual therapy, mechanotherapy.
Diet
Diet for osteoarthritis should be as balanced and rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids, proteins, trace elements. It is recommended to include in the diet fresh fish, vegetable oils, cheese, dairy products, meat, fresh vegetables and fruits.
From the diet should exclude flour products and "fast" carbohydrates, chocolate, coffee, alcohol, pork, fatty and spicy dishes.
Surgical treatment
If conservative treatment has not led to expected result or osteoarthritis diagnosed at an advanced stage, when there are pronounced degenerative changes of the joint with severe mobility limitation, then the patient is prescribed surgery.
Surgical treatment of osteoarthritis is carried out in several ways:
- Puncture of the affected joint – this method is both diagnostic and therapeutic. Specimen collection synovial fluid allows to define precisely the nature of the origin of the disease and to select effective drug. During the operation of the puncture into the joint cavity administered corticosteroids and various anti-inflammatory drugs, which instantly eases the pain and relieves the load on the joint.
- Arthroscopy in the joint cavity, the arthroscope for a thorough examination of the joint from the inside. During the operation, the doctor can remove growths on the bones and various neoplasms.
- Osteotomy – the operation of the joint bones a little adjusting special tools and fixed in the correct position, which allows not only to restore motor function, but also to relieve the patient from discomfort and severe pain.
- Joint replacement is a destroyed joint is removed and in its place install a prosthesis of high quality material, which fully assumed the functions of the lost joint, provide full mobility of the limb and save the patient from pain.
Prevention
Prevention of osteoarthritis is the integrated campaign:
- maintaining a healthy and active lifestyle;
- rational and adequate nutrition;
- elimination of bad habits;
- prevention of injuries and damage to the joints;
- timely treatment of inflammatory processes.
People from risk groups should be especially attentive to the slightest changes in the joints and the appearance of pain, crunching and creaking immediately seek the advice of traumatologist-orthopedist.



































